AI’s authority in academic and scientific research is an established notion. Today, analysts have access to AI tools that are invaluable for research across various disciplines. These tools are helping streamline literature reviews, data analysis, writing, and even generating hypotheses. We have reviewed hundreds of AI tools for academic and research studies and shortlisted 50 for our deeper analysis. These AI tools cover a wide range of needs for researchers from managing citations and conducting literature reviews to analyzing data and enhancing writing. Whether you’re looking for tools for paper discovery (like Research Rabbit, Semantic Scholar, or Inciteful), data analysis (e.g., Google Colab, DataRobot), or writing assistance (e.g., Grammarly, Ref-N-Write), these platforms can streamline the research process and boost productivity.
Reviewed and rated by our expert AI analysts, below are some of the top 10 AI tools (PLUS, A FEW MORE) commonly used in academic and scientific research:
#1 Google Colab
Powered by Google DeepMind, Google Colab (derived from “collaboratory“) is a cloud-based platform for writing and running Python code, which is particularly popular in data science, machine learning, and AI research. It offers a free Jupyter Notebook environment that allows users to write and execute code in Python, with the added benefit of free access to GPUs and TPUs. Researchers use Google Colab for running complex computational models, data analysis, and experimenting with machine learning algorithms. The platform also allows easy collaboration, enabling multiple users to work on the same codebase in real time. As it integrates with Google Drive, users can easily share their notebooks and results.
Benefits:
Colab notebooks run code on Google’s cloud infrastructure, allowing you to tap into the power of Google’s hardware, including GPUs and TPUs, no matter the specs of your local machine. All you need is a browser.
For instance, if you’re waiting for pandas code to complete, you can switch to a GPU runtime and use libraries like RAPIDS cuDF to accelerate performance without code changes.
Analysts review for Google Colab
Strengths:
- Zero Setup & Accessibility: No installation is required. It is accessible directly through a browser.
- Free GPUs & TPUs: Provides free access to powerful GPUs and TPUs for accelerated computation, ideal for machine learning and deep learning tasks.
- Easy Collaboration: Real-time sharing and collaboration, similar to Google Docs, perfect for team-based academic and research projects.
- Google Ecosystem Integration: Seamlessly integrates with Google Drive, GitHub, Kaggle, and cloud storage for easy data access.
- Wide Library Support: Supports popular Python libraries (e.g., Pandas, TensorFlow, PyTorch) and easy library installation.
Limitations:
- Resource Limits: The free tier has GPU access limits and session duration restrictions, which may be a bottleneck for large-scale tasks.
- Storage Concerns: Limited free storage on Google Drive for large datasets, though external storage options are available.
- Limited Customization: Some restrictions on installing specific system packages or managing complex environments.
Conclusion:
- Google Colab is a powerful, accessible tool for data science, machine learning, and academic research with collaborative features and free GPU access.
- Best suited for quick experiments and prototyping, but may have limitations for more complex projects.
AITechnology Insights’ AI-Authority Rating: 10/10
#2 Scite: AI for Research
Scite is an AI-powered research tool designed to assist researchers in discovering, analyzing, and organizing academic papers. Recommended by Purdue University, subscription is required to gain access to the libraries.
Benefits:
By leveraging advanced AI algorithms, Scite goes beyond traditional citation tracking, providing “Smart Citations” that show whether a paper is cited, and how it is cited—whether it supports, contrasts, or mentions the work in question. This tool helps researchers identify key papers, understand relationships between studies, and gain deeper insights into the scientific literature.
It highlights whether a paper supports, contradicts, or merely mentions another paper, making it easier to understand the context of references. Researchers can use Scite for literature review purposes, as it offers a deep dive into the relationship between research papers, providing more insight than traditional citation counting. The AI’s citation graph is particularly useful in mapping out key research trends and identifying influential works.
Scite also offers a feature to track research updates, helping users stay up-to-date with the latest papers in their field.
Analyst Review for Scite
Strengths:
- Smart Citations: Scite’s AI-powered citation analysis allows users to see whether a paper supports, contradicts, or merely mentions other research, making it more useful than traditional citation tracking.
- Enhanced Literature Review: The tool helps researchers quickly identify relevant papers and understand their context in the broader body of work, accelerating the literature review process.
- AI-Powered Insights: Scite’s AI provides actionable insights and trends within scientific papers, helping researchers stay up-to-date on emerging topics and key findings.
- Collaboration and Sharing: Scite makes it easy to collaborate with others by allowing users to share research, insights, and curated collections of papers.
- Customizable Alerts: Users can set up alerts for new papers, citations, or research trends, ensuring they never miss out on important developments in their field.
Limitations:
- Limited Access to Full Texts: Scite does not always provide access to the full text of papers, as it relies on publicly available data or subscriptions for access, which can be a limitation for some users.
- Learning Curve: For new users, it can take a little time to understand how to fully leverage “Smart Citations” and AI-driven insights, especially for those who are accustomed to traditional research tools.
- Subscription Costs: While Scite offers a free version, more advanced features and deeper access require a paid subscription, which may be a barrier for some users, particularly in academic settings with limited funding.
Conclusion:
Scite is a powerful AI tool that revolutionizes how researchers engage with academic literature. Its innovative Smart Citations feature, combined with AI-driven insights and advanced literature management, provides a more effective and efficient way to conduct research. While it has some limitations in terms of access to full texts and a learning curve for new users, its potential for enhancing research workflows and accelerating the discovery of key studies makes it an invaluable tool for researchers and academics.
AITechnology Insights’ AI-Authority Rating: 9.9/10
#3 Zotero
Zotero is a free, open-source reference management tool designed for organizing research sources. It allows users to collect, manage, cite, and share their research materials, including articles, books, websites, and other resources.
Benefits:
Zotero automatically saves citation information from web pages, databases, and PDFs, making it easy to build and manage a personal library. One of its standout features is its ability to create bibliographies and citations in various formats (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.). Additionally, Zotero enables collaborative research by allowing users to create shared libraries for team-based projects, making it ideal for researchers working in groups. The browser plugin automatically extracts metadata from research materials, simplifying the citation process.
Analyst Review for Zotero
Strengths:
- Automatic Citation Management: Zotero automatically extracts citation information from academic papers, websites, and databases, saving researchers time in collecting and formatting references.
- Seamless Integration: Zotero integrates well with web browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari) and word processors (Microsoft Word, Google Docs), making it easy to save and insert citations directly into documents.
- Collaborative Features: Zotero allows users to create shared libraries and collaborate with colleagues, making it ideal for team-based research projects and group writing.
- Open-Source & Free: Zotero is open-source and free to use, with no paid subscription required for core features, making it an accessible tool for individual researchers and academic institutions.
- Organizational Tools: Users can organize references into collections and tag items for easier retrieval, while the built-in search function helps quickly locate specific papers or resources.
Limitations:
- Storage Limits: While Zotero offers unlimited storage for references, free users are limited to 300MB of cloud storage for PDFs and attachments. Additional storage requires a paid subscription.
- Limited Advanced Features: Zotero’s feature set may not be as advanced as some paid reference management tools, particularly for users requiring detailed citation styles, advanced formatting options, or project-specific workflows.
- Learning Curve for New Users: Although Zotero is generally user-friendly, beginners may need some time to familiarize themselves with its interface, especially when organizing large libraries or using advanced features.
- Occasional Syncing Issues: Some users report occasional syncing issues between devices, particularly when using large libraries or when updates are pushed out.
Conclusion:
Zotero is a robust and user-friendly tool for managing citations, references, and research documents. Its seamless integration with browsers and word processors, coupled with strong organizational features, makes it an ideal solution for researchers at all levels. While it does have some limitations around storage and advanced features, its open-source, free-to-use model, and collaborative capabilities make it an excellent choice for academic research.
AITechnology Insights’ AI-Authority Rating: 9.87/10
#4 Research Rabbit
Research Rabbit is a visual research discovery tool that helps researchers explore academic papers and discover relationships between them.
Benefits:
Research Rabbit visualizes the connections between papers in an easy-to-understand graph format by analyzing citations, references, and keywords. Researchers can start by entering a few key papers or topics of interest, and the tool will automatically generate a network of related papers. This approach helps uncover papers that may not have been found using traditional search engines or databases. The tool’s ability to explore relationships between papers makes it ideal for literature reviews and gaining an overview of a research topic’s development over time.
It simplifies the literature review process, helping researchers find related work quickly and efficiently, all while offering a user-friendly interface and seamless integration with academic databases.
Analyst Review for Research Rabbit
Strengths:
- AI-Powered Paper Discovery: Research Rabbit uses AI to generate visual citation networks, enabling researchers to see connections between papers that they might not have discovered through traditional searches.
- Intuitive Visualization: The platform offers interactive, dynamic maps that visually represent the relationships between academic papers, helping users quickly identify key references and trends in a research field.
- Efficient Literature Review: Research Rabbit helps users identify gaps in the literature and avoid redundant studies by exploring citation connections, streamlining the literature review process.
- Easy Integration: Research Rabbit integrates with databases like Google Scholar and CrossRef, allowing for easy access to papers and citations from trusted sources.
- Collaborative Features: The tool enables researchers to share their discovery maps and research insights with colleagues, fostering collaboration and collective learning.
Limitations:
- Limited Access to Full Texts: Like many research tools, Research Rabbit does not provide access to the full text of academic papers, which can limit its usefulness when detailed reading is required.
- Narrow Scope: The tool’s capabilities are primarily focused on citation and reference relationships, so it may not provide as comprehensive an analysis as traditional research tools, including access to full-text papers and broader context.
- Learning Curve: While the visualization tool is intuitive, researchers unfamiliar with citation mapping might need time to fully grasp how to interpret the network and leverage the tool effectively.
- Database Access: While it integrates with well-known databases, access to some sources may still be limited, and certain papers may not appear due to database restrictions.
Conclusion:
Research Rabbit is an innovative tool that simplifies the research process by using AI to create citation and reference networks, helping researchers quickly identify relevant studies and visualize relationships in academic literature. Its AI-driven discovery and intuitive mapping interface make it a valuable tool for anyone conducting a literature review or exploring new research areas. However, its focus on citation analysis and the lack of full-text access may limit its utility for researchers needing in-depth information from primary sources.
AITechnology Insights’ AI-Authority Rating: 9.85/10
#5 Inciteful
Researchers use Inciteful in their academic and scientific works to uncover gaps in the literature, track the evolution of research topics, and identify highly cited works to cover for the ones missed in traditional literature searches.
Benefits:
Inciteful is an AI-powered research tool designed to help researchers discover, explore, and visualize academic papers in a dynamic and interconnected manner. Using citation and co-citation analysis, Inciteful offers advanced search and exploration features, enabling users to identify influential papers and key connections between studies. It allows researchers to track the evolution of research topics, find overlooked papers, and gain deeper insights into their field of study. The tool is particularly useful for creating a more comprehensive and targeted literature review, providing a clearer view of research trends and scholarly impact.
Analyst Review for Inciteful
Strengths:
- Citation and Co-Citation Analysis: Inciteful’s advanced citation analysis helps researchers identify influential papers and trace the development of research topics through citation networks.
- Interactive Visualization: Inciteful offers an interactive citation graph that lets users visualize relationships between papers, uncover hidden connections, and better understand how research evolves.
- Discovery of Overlooked Papers: By highlighting papers with strong co-citations and links to related studies, Inciteful helps researchers discover relevant works that may have been missed in traditional searches.
- Comprehensive Literature Review: The platform streamlines the literature review process by suggesting relevant studies, visualizing citation networks, and allowing users to quickly identify key papers and emerging trends.
- Intuitive User Interface: Inciteful’s user-friendly interface makes it easy to search, explore, and interact with academic papers and their citations, providing an intuitive experience for users of all expertise levels.
Limitations:
- Limited Full-Text Access: While Inciteful offers citation and co-citation insights, it does not provide direct access to full-text papers, which may limit its utility for researchers who need detailed readings of specific studies.
- Database Coverage: Inciteful’s database might not cover all journals or academic fields comprehensively, and some niche papers may be missing, depending on the available data sources.
- Learning Curve for New Users: Although the tool is intuitive, some users may need time to fully understand the advanced citation graph features and how to navigate the complex network of references.
- Focus on Citation Analysis: Inciteful is focused on citation and co-citation data, so it may not provide the full range of research insights (e.g., qualitative data or methodologies) that some researchers may need.
Conclusion:
Inciteful’s ability to identify key papers, track the evolution of research topics, and uncover overlooked studies makes it an excellent choice for researchers conducting literature reviews or exploring new research areas. While it does have limitations in terms of full-text access and database coverage, its focus on citation networks and its intuitive interface makes it a valuable resource for academics and researchers seeking to gain deeper insights into their field.
AITechnology Insights’ AI-Authority Rating: 9.81/10
#6 Mendeley
Mendeley is a reference manager and academic social network for academicians and research groups.
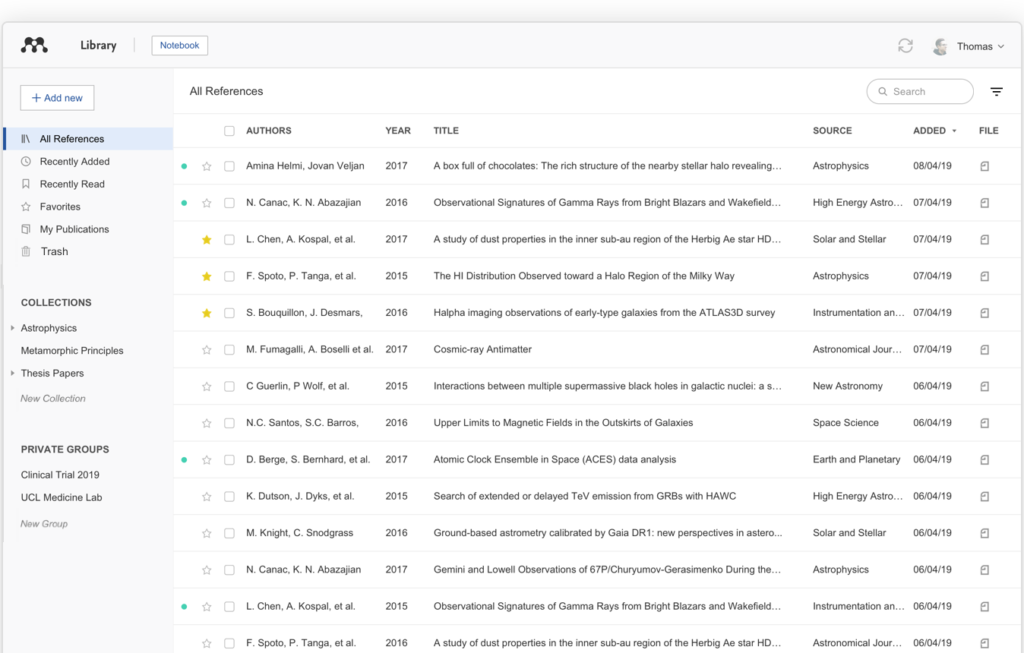
Image: Mendeley Reference Manager
Benefits:
Mendeley is a widely used reference management tool and academic social network designed to help researchers organize, share, and discover research papers. It enables users to collect and manage citations, generate bibliographies, and collaborate with other researchers. Mendeley offers a powerful PDF annotation feature, allowing users to highlight, comment, and tag PDFs directly within the platform. Additionally, Mendeley’s citation manager integrates seamlessly with Microsoft Word and other word processors, making it easier for users to insert citations and format bibliographies. Mendeley’s social network also provides a platform for researchers to collaborate and share research findings within a global academic community.
Analyst Review for Mendeley
Strengths:
- Comprehensive Reference Management: Mendeley allows users to store, organize, and manage a large library of references and research papers in a single place, streamlining the research process.
- PDF Annotation and Note-Taking: Users can highlight, annotate, and take notes on PDFs, making it easier to engage with research material and organize thoughts for future writing.
- Collaborative Features: Mendeley supports group collaboration, enabling researchers to share papers, notes, and ideas with colleagues or academic teams, facilitating group research projects.
- Citation Integration: Mendeley integrates with word processors (e.g., Microsoft Word, LibreOffice), allowing users to automatically generate citations and bibliographies in multiple citation styles with ease.
- Academic Social Network: Mendeley connects researchers globally, providing access to a network of academic professionals, sharing papers, and collaborating on projects.
- Cloud Syncing: Mendeley offers cloud-based syncing, ensuring that your references and annotations are accessible across multiple devices.
Limitations:
- Storage Limits: While Mendeley offers free storage for documents, the free plan limits storage to 2GB, which can quickly fill up for users with large research libraries. Paid plans are available for additional storage.
- Limited Full-Text Search: While Mendeley offers a robust search feature for references, it doesn’t always provide full-text access or the most comprehensive indexing, especially for niche or non-open-access journals.
- Complex Interface for New Users: New users may find Mendeley’s interface to be overwhelming at first, especially with its wide range of features. There is a learning curve to mastering the tool for optimal use.
- Syncing Issues: Some users report occasional syncing problems across devices, particularly when working with large libraries or multiple group collaborations.
Conclusion:
Mendeley’s cutting-edge reference management tool helps researchers manage citations, annotate PDFs, and collaborate with other scholars. Its seamless integration with word processors, citation tools, and collaborative features make it a popular choice for academics across disciplines. While it offers strong features for citation management and collaboration, limitations around storage and full-text access may be a concern for some users. Overall, Mendeley is an excellent tool for managing research materials, staying connected with the global academic community, and streamlining the writing and publication process.
AITechnology Insights’ AI-Authority Rating: 8.7/10
#7 Semantic Scholar
Semantic Scholar is a free AI-powered research tool designed to help researchers quickly discover and explore academic papers. Developed by the Allen Institute for AI, it leverages machine learning algorithms to provide relevant paper recommendations, identify influential citations, and offer deep insights into research trends.
Benefits:
With features like “Semantic Search” and “Citation Graphs,” Semantic Scholar helps users find high-quality research faster, prioritize influential studies, and track the evolution of research topics. The platform also provides full-text access to many open-access papers and offers citation analysis features to help researchers understand how their work fits within the broader academic landscape.
Analyst Review for Semantic Scholar
Strengths:
- AI-Powered Search and Recommendations: Semantic Scholar uses AI to provide smarter paper recommendations, improving the quality and relevance of search results by understanding the content of papers beyond just keywords.
- Citation Graphs: The platform allows users to explore citation graphs that visually represent the relationships between papers, helping researchers identify key studies and influential citations in their field.
- Free Access to Full Texts: Many papers on Semantic Scholar are open access, making it easier for users to access full-text versions of academic papers without paywalls.
- Influence and Impact Scores: Semantic Scholar provides “Semantic Search” results that highlight highly-cited and influential papers, helping users prioritize their reading. The “Field Citation Ratio” (FCR) shows how frequently papers are cited relative to others in their field, offering insights into their impact.
- User-Friendly Interface: The platform offers an intuitive, easy-to-navigate interface, with quick search capabilities, filters, and sorting options to help users locate papers efficiently.
- Advanced Search Filters: Semantic Scholar offers advanced search filters (e.g., year, citation count, paper type) to help refine results, making it easier for researchers to find the most relevant papers in their field.
Limitations:
- Limited Access to Non-Open-Access Papers: While many papers are available in full-text, access to non-open-access articles is often limited, and users may encounter paywalls or restricted access to some sources.
- Smaller Database Compared to Competitors: Semantic Scholar’s database, while growing, may not be as comprehensive as other academic databases like Google Scholar, Scopus, or PubMed, particularly in niche fields.
- Dependence on Open Access: The platform’s focus on open-access papers may limit access to content behind paywalls, reducing the diversity of available studies.
- Occasional Inaccuracies in Metadata: Some researchers report that the metadata for certain papers (such as citation counts or publication details) may be inaccurate or incomplete, which can affect the reliability of citation analysis.
Conclusion:
Semantic Scholar is an AI-powered research tool that offers a highly efficient way to search for, discover, and analyze academic papers. Its AI-driven recommendations, citation graphs, and user-friendly interface make it a valuable resource for researchers seeking to stay up-to-date with the latest literature and understand the impact of their work. While it excels in offering free access to many papers and improving search relevancy, the platform’s reliance on open-access content and occasional metadata inaccuracies may limit its utility for researchers requiring more comprehensive database coverage or access to proprietary sources. Despite these limitations, Semantic Scholar remains an excellent tool for academics looking to streamline their research process and explore emerging trends in their field.
AITechnology Insights’ AI-Authority Rating: 8.65/10
#8 Scholarcy
Scholarcy is an AI-powered tool designed to help researchers quickly summarize and analyze academic papers. By processing research articles, this AI tool for technical research generates concise summaries, key points, and highlights, allowing users to understand complex papers more efficiently.
Benefits:
Scholarcy uses natural language processing (NLP) to extract important information, such as key concepts, figures, tables, and references. Scholarcy is particularly useful for quickly assessing the relevance of papers, streamlining literature reviews, and improving the speed of research workflows. Additionally, it integrates with reference managers like Zotero and Mendeley to automatically organize and annotate papers, enhancing overall research productivity.
Analyst Review for Scholarcy
Strengths:
- AI-Powered Summarization: Scholarcy uses advanced NLP techniques to generate summaries of academic papers, making it easier for researchers to quickly grasp the key findings, methods, and conclusions.
- Automatic Extraction of Key Information: The tool extracts critical components of research papers, such as figures, tables, and references, helping users identify important details at a glance.
- Efficient Literature Review: Scholarcy simplifies the process of reviewing literature by providing condensed summaries of multiple papers, allowing researchers to quickly compare and contrast studies.
- Reference Management Integration: Scholarcy integrates with popular reference management tools like Zotero, Mendeley, and EndNote, allowing users to save, organize, and annotate papers directly within their workflow.
- Customizable Summaries: The tool lets users adjust the summary length and level of detail based on their needs, offering flexibility for both quick overviews and deeper analysis.
- Time-Saving: By automating the summarization process, Scholarcy saves researchers significant time, enabling them to focus on more critical tasks like hypothesis testing and data analysis.
Limitations:
- Limited Full-Text Access: While Scholarcy generates summaries and highlights, it does not always provide full-text access to papers, especially if they are behind paywalls or are not open access.
- Quality of Summaries: While AI-generated summaries are useful, they may occasionally miss nuanced details or the full context of complex papers, which can affect their accuracy for more in-depth analyses.
- Not a Substitute for Deep Reading: Scholarcy’s summaries are great for quick overviews, but they cannot fully replace deep reading and critical evaluation of the entire paper, especially for complex or highly specialized topics.
- Dependence on PDF Quality: Scholarcy’s effectiveness depends on the quality of the PDF document. Scanned or poorly formatted papers may yield less accurate results, as the tool relies on text extraction from the document.
Conclusion:
Scholarcy is an innovative AI tools for academic and scientific research. It accelerates the research process by providing AI-generated summaries, extracting key information, and streamlining literature reviews. It is especially valuable for researchers who need to quickly evaluate and synthesize large volumes of academic papers. While it cannot replace deep, thorough reading, it significantly speeds up the process of understanding and organizing research, making it an excellent tool for time-strapped academics. Its integration with reference managers and customizable summaries add further value, making it a versatile addition to a researcher’s toolkit.
AITechnology Insights’ AI-Authority Rating: 8.45/10
#9 Clarivate Web of Science
Web of Science is one of the most comprehensive research databases, offering access to scholarly articles, conference proceedings, patents, and more. With AI-enhanced features, Web of Science allows researchers to explore citation data, identify influential papers, and track trends across scientific disciplines. Researchers can use the platform to analyze citation patterns, measure the impact of their work, and discover new research avenues. Its citation index is widely used in academia to assess the influence and relevance of research articles. Web of Science also features robust search capabilities, allowing researchers to find relevant papers based on author, title, journal, or subject.
Benefits:
Clarivate Web of Science is a comprehensive, AI-powered research platform that provides access to an extensive collection of scholarly articles, journals, conference proceedings, and other academic resources. It offers advanced citation indexing and search functionalities, enabling researchers to discover high-impact publications, track citation patterns, and identify emerging trends in their fields. Web of Science’s machine learning algorithms help to refine search results and provide personalized recommendations based on the user’s research interests.
Additionally, its citation analysis and impact factor tools help researchers assess the quality and influence of published works, while its integration with reference management tools like EndNote facilitates seamless citation tracking.
Analyst Review for Clarivate Web of Science
Strengths:
- Comprehensive Database: Web of Science hosts an extensive collection of high-quality scholarly content across various disciplines, including journals, conference papers, and patents, making it a one-stop resource for academic research.
- Advanced Citation Indexing: The platform offers detailed citation analysis, helping researchers track the influence and relevance of published works through citation counts and citation networks.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI algorithms personalize search results and paper recommendations, improving the relevance of the resources presented based on user activity and research interests.
- Citation Impact Tools: Web of Science offers powerful tools like the Journal Impact Factor (JIF) and citation reports that allow users to assess the academic impact of journals and individual papers, guiding research decisions.
- Integration with Reference Management: The tool integrates with popular reference management software, such as EndNote, allowing researchers to organize citations and manage their bibliographies with ease.
- Advanced Search Filters: Web of Science provides robust filtering options based on keywords, citation counts, author, publication type, and more, allowing researchers to narrow down results to the most relevant studies.
Limitations:
- Subscription-Based Access: Unlike some other research tools, Web of Science operates on a subscription model, meaning access to full-text papers and advanced features may be limited for users without institutional or personal subscriptions.
- Learning Curve: The breadth of features and sophisticated search functionalities can make Web of Science challenging for new users to navigate efficiently without a learning curve.
- Limited Open Access Content: While Web of Science provides access to many high-impact papers, the platform has limited access to open-access resources compared to other free platforms like Google Scholar.
- Occasional Data Gaps: Despite its broad coverage, Web of Science may not index every niche journal or regional publication, leading to potential gaps in its database for highly specialized or emerging topics.
- High Cost for Individual Users: Access for individual researchers can be expensive without institutional subscriptions, making it less accessible for independent scholars or smaller research teams.
Conclusion:
Clarivate Web of Science’s AI-enhanced research platform designed for serious academic researchers and institutions. Its extensive database, advanced citation indexing, and personalized recommendations make it an invaluable resource for tracking influential studies, identifying emerging trends, and assessing the impact of academic work. However, its subscription-based model and limited access to open-access content may restrict access for some users, particularly independent researchers. Despite these limitations, Web of Science remains one of the most authoritative platforms for academic research and citation analysis.
AITechnology Insights’ AI-Authority Rating: 9/10
#10 ArXiv
ArXiv is a popular open-access preprint server for research papers in the fields of physics, mathematics, computer science, quantitative biology, quantitative finance, and more. The platform has millions of preprints, and with AI tools, researchers can efficiently browse, filter, and discover the latest developments in their fields.
Benefits:
ArXiv is a widely used open-access repository for research papers, particularly in the fields of physics, mathematics, computer science, quantitative biology, and related disciplines. Founded by Cornell University, ArXiv allows researchers to upload and freely share preprints of their work before they undergo peer review. The platform has become an essential tool for academics, offering immediate access to cutting-edge research and fostering collaboration within scientific communities. With its simple, user-friendly interface and free access to all content, ArXiv democratizes research dissemination, making it easier for researchers to stay up-to-date on the latest developments in their fields. ArXiv also supports AI-powered search functionalities, helping users quickly find relevant papers based on keywords, citations, and topic areas.
Analyst Review for ArXiv
Strengths:
- Open Access & Free Content: ArXiv provides free access to thousands of research papers, enabling anyone with an internet connection to view the latest preprints in various scientific fields.
- Preprints for Early Dissemination: Researchers can share their work before peer review, allowing for early dissemination of findings and enabling feedback from the global scientific community.
- Wide Range of Disciplines: ArXiv hosts preprints across multiple fields, including physics, computer science, mathematics, and more, making it a go-to resource for interdisciplinary research.
- Rapid Access to Cutting-Edge Research: With new papers uploaded daily, ArXiv allows researchers to access the latest developments in their fields, often before they are published in traditional academic journals.
- Advanced Search and Filtering: ArXiv provides AI-enhanced search capabilities, making it easier for users to find specific papers based on topics, authors, keywords, and more.
- Collaboration and Networking: Researchers can collaborate, comment on, and share preprints, fostering a culture of collaboration and speeding up the research process.
Read AITechnology Authority news: Tetherball Memecoin ($TBALL) Launches Athena.tball: AI Bot for Community Engagement
Limitations:
- Lack of Peer Review: ArXiv hosts preprints that have not yet undergone peer review, meaning the quality and accuracy of the research are not guaranteed. This can lead to concerns about the reliability of the findings.
- Overwhelming Volume of Papers: Given the high volume of preprints submitted daily, it can be difficult for users to sift through the content to find the most relevant or impactful papers in their area of interest.
- Limited Support for Full-Text Access: Although ArXiv provides access to the full text of preprints, some papers are often missing supplementary materials, datasets, or detailed appendices, which can limit the overall value of the research for practical use.
- No Formal Versioning or Editing: Unlike peer-reviewed journals, ArXiv does not provide a formal versioning system, meaning the same paper may be updated multiple times without clear indication of revisions or changes.
- Focus on Preprints: ArXiv primarily hosts preprints, which may not always reflect the final, peer-reviewed version of a study. Researchers must often cross-reference papers with journal versions for confirmed results.
Conclusion:
ArXiv is a powerful and essential platform for researchers looking to quickly access and disseminate new findings in the scientific community. Its open-access nature, wide disciplinary scope, and rapid publication of preprints make it a go-to resource for staying up-to-date on emerging research. However, because papers are not peer-reviewed and can be updated multiple times without formal versioning, researchers must approach the platform with a critical eye, especially when using preprints for foundational or applied research. Despite these limitations, ArXiv remains an invaluable tool for academic researchers and is an integral part of modern scientific publishing.
AITechnology Insights’ AI-Authority Rating: 8/10
More options:
- Microsoft Academic (now integrated with Semantic Scholar)
- Sci-Hub
- ChatSonic
- CiteSpace
- PubMed
- medRxiv
- BioRxiv
- ResearchGate
Conclusion
The rise of AI tools for academic and scientific research has revolutionized how scholars conduct their work, offering new methods to streamline workflows, boost productivity, and extract deeper insights from vast bodies of literature. Tools like Zotero and Mendeley simplify reference management, while platforms like Litmaps, Elicit, and CiteSpace enable researchers to visualize citation networks and track the evolution of research topics. For those conducting systematic reviews, tools like Knotorys and RoboReview automate much of the review process, saving researchers valuable time while ensuring comprehensive results.
AI-powered writing assistants such as Writefull and QuillBot are improving academic writing by providing suggestions for better clarity, grammar, and coherence, while platforms like EndNote and RefWorks streamline citation generation and document organization. Meanwhile, tools like Google Scholar and PubMed continue to serve as essential resources for literature discovery, supported by AI that enhances search relevance and citation analysis.
As the research landscape becomes more data-driven and collaborative, AI tools will play an increasingly important role in managing complex datasets, improving research reproducibility, and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration. These technologies help democratize access to knowledge, ensuring that researchers from all backgrounds can engage in global scientific discussions. By integrating AI into research workflows, scholars can focus on the creative and critical thinking aspects of their work, while leaving the repetitive, time-consuming tasks to AI.
In the years to come, AI and academic research will become increasingly intertwined, transforming the future of scholarship. Researchers who leverage these tools will be better positioned to stay ahead of the curve, drive innovation, and contribute meaningfully to the next wave of scientific discovery.
Recommended AI Authority Insights: ABBYY MVPs: Shaping the Future of DevOps and AI-Driven Automation
To share your insights, please write to us at news@intentamplify.com